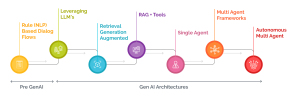
The P&C insurance industry is amidst a revolution in customer self-service led by the tremendous growth of Generative AI architectures. In this blog series, we will explore the evolution of these AI systems, from the early rule-based systems to the sophisticated multi-agent frameworks of tomorrow, while outlining the potential impact on the industry.
In this blog, we will dive deep into understanding how today’s service applications have evolved to the now standard LLM+RAG+Tools based frameworks.
The pre-gen AI era: rules-driven systems
The intelligence in solutions for customer service traces back to rule-based technologies like Decision Trees, Scorecards, and even simple if-then frameworks. These early solutions allowed predictable and consistent responses based on basic Natural Language Processing methods applied towards inferring customer input. Their fixed nature had them dealing with pre-defined questions that were not suited for complex or even ad-hoc queries.
The characteristics that defined these systems:
- Application of decision trees, decision tables, and finite state machine
- Limited capability to handle queries outside predefined rules
- Basic functionalities like automated policy renewal reminders and easy claim status inquiries.
While these systems laid the groundwork for intelligent customer service applications, their limitations soon became apparent as stakeholder expectations evolved.
The LLM Revolution: Leveraging Language Models
The next giant stride was through the usage of large language models. LLMs helped AI move from entirely abstract modeling of conditions to understanding and generating human-like text, greatly expanding the range of customer queries that could be addressed.
LLMs brought several advantages, such as:
- Better context handling; subtler interpretation of a query
- More Inherent Natural Language Understanding and Generation
- Additional services including explanations of intricate policy language and providing individualized advice.
Although LLMs posed novel challenges associated with the dangers of hallucination and they lacked expert knowledge in the insurance domain, they remained the best fit and were adopted very quickly by the industry.
RAG: High Precision and Relevance
To address the limitations of stand-alone LLM based solutions, the industry witnessed a new set of techniques – Retrieval-Augmented Generation or RAG for short. RAG bought the best of an LLM with the ability to fetch information relevant directly from curated knowledge bases.
- Improved correctness by anchoring answers from verified sources
- Improved range with access to specific, up-to-date information.
- Enhanced understanding of company-specific policies and procedures.
RAG systems greatly reduced the risk of transmitting dubious information to customers, a critical requirement in the highly regulated insurance industry.
Present Frontier: RAG + Tools
The latest evolution in this trend is the integration of RAG systems with external tools and APIs. This advancement enables AI systems not only return information but to perform real-time operations; they can even access data that resides in external datasets.
RAG + Tools systems have several advantages.
- Allows for real-time data retrieval and action execution
- Enables LLMs to interact with external tools and APIs
- Enhances ability to perform complex tasks like policy lookups or claim status checks
This evolution of Gen AI architectures in P&C insurance customer service has been marked by significant strides in natural language understanding, accuracy, and actionability. From the limited scope of rules-driven systems to the sophisticated RAG + Tools solutions, each phase has brought us closer to the ideal of efficient, accurate, and comprehensive customer service.
In Part 2 of this series, we’ll explore the emerging architectures poised to shape the future of AI in P&C insurance customer service, including single-agent systems, multi-agent frameworks, and autonomous multi-agent systems. We’ll examine how these ‘Agentic Architectures’ promise to simplify customer interactions, streamline complex processes, and potentially reshape the insurance industry landscape.